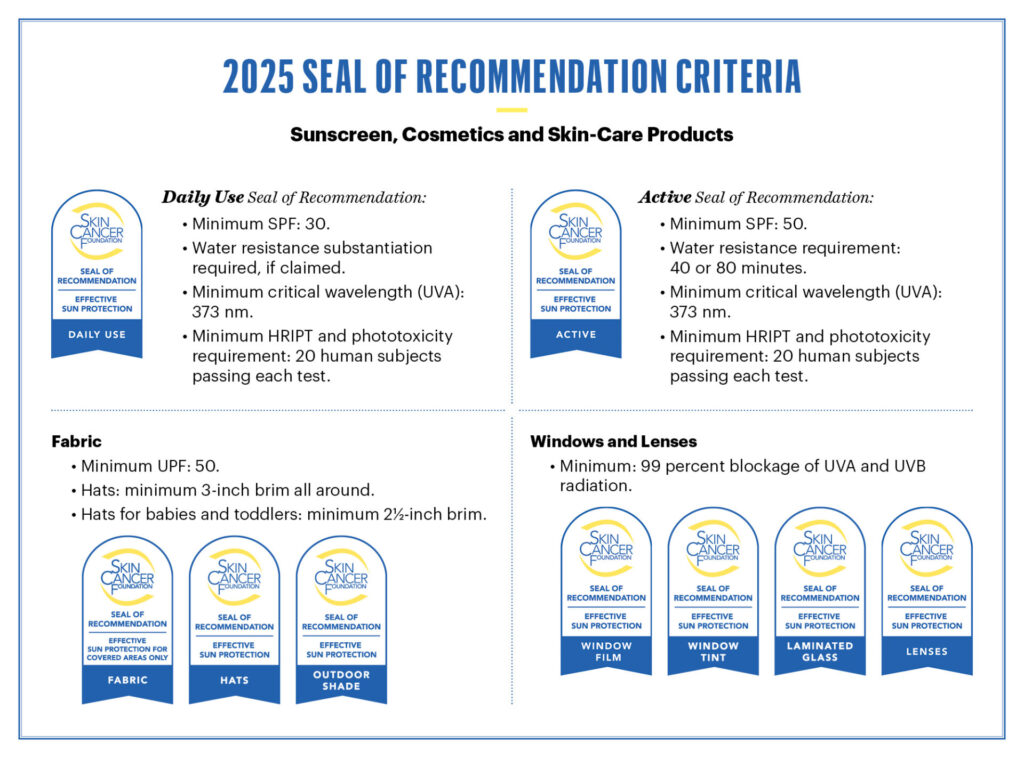
In 2025, The Skin Cancer Foundation introduced updated criteria for our Seal of Recommendation.
Based on the latest science, our Seal of Recommendation offers the highest standard of sun protection. Wondering what all these terms mean, and why they are so important to your skin health? We’ve got you covered!
SPF
What it is: SPF stands for Sun Protection Factor. The number tells you how long the sun’s UVB rays would take to redden your skin if you apply the sunscreen exactly as directed compared with the amount of time without sunscreen. So, if you use an SPF 30 product correctly, it would take you 30 times longer to burn than if they didn’t use sunscreen.
How it’s tested: A sunscreen’s SPF is tested in vivo (on human subjects). Two small patches of the subject’s skin are exposed to a controlled amount of UV light, the first unprotected and the second after sunscreen is applied. The researchers then calculate the SPF based on how long it takes for the unprotected versus protected skin to redden. While there are methods to test SPF in a lab (in vitro), they are not currently accepted by the FDA or the Seal of Recommendation.
What’s changed: The minimum SPF for products with the Daily Use Seal of Recommendation increased from SPF 15 to SPF 30. For sunscreen products with the Active Seal of Recommendation, the SPF requirement increased from SPF 30 to 50.
Critical Wavelength
What it is: Wavelengths along the solar spectrum affect the skin in different ways. Exposure to UVB and UVA rays, measured in nanometers (nm), each one-billionth of a meter, causes damage that can lead to skin cancer. The critical wavelength (CWL) test provides information about the breadth of UV coverage a sunscreen provides.
How it’s tested: Sunscreen is evenly applied to a glass slide and exposed to UV light. Using a device, researchers can measure the UV absorption of a sunscreen. To be labeled “broad spectrum,” a sunscreen must protect against both UVB (the shorter waves mainly responsible for sunburn) and UVA rays (the slightly longer rays mainly responsible for tanning but that also increase risk for skin cancer). This test is different from an SPF value, since SPF only measures a product’s protection against UVB rays.
What’s changed: To earn the Seal of Recommendation, sunscreen products must demonstrate a minimum CWL (UVA protection) of 373 nm, up from the previous requirement of 370 nm.
HRIPT
What it is: This is a patch test that evaluates the potential for a sunscreen product to cause irritation or allergic reactions on the skin of human subjects.
How it’s tested: Researchers apply small patches of the test substance to subjects’ skin (usually on their backs) and leave the substance in place for a specified amount of time. When the substance is removed, the researchers look for and record any signs of allergy or irritation.
Phototoxicity
What it is: When a substance reacts with UV light to cause skin irritation.
How it’s tested: Small amounts of the test substance are applied to subjects’ skin, which is then exposed to UV light to monitor for signs of irritation.
UPF
What it is: UPF stands for ultraviolet protection factor. This rating indicates how much UVA and UVB radiation a fabric allows to reach your skin. Clothing or a hat with a UPF of 50, for example, blocks 98 percent of the sun’s rays and allows 2 percent (1/50th) to penetrate.
How it’s tested: Using special instruments, a laboratory tests how much UV radiation penetrates a fabric, tested both wet and dry to ensure consistent protection.
What’s changed: Fabrics (both clothing and outdoor shade products) earning the Seal of Recommendation must demonstrate a minimum UPF requirement of 50, up from the previous requirement of 30.
UV Window Film & Tint
What it is: UV window film is a specialized treatment applied to glass that blocks 99 percent of UV rays.
How it’s tested: UV window film and tint are tested in a laboratory with specialized equipment that measures the amount of radiation that passes through the treated glass.
Related content:
Be Safe in the Sun: Seek the Seal!
Seal of Recommendation
Recommended Products
Your Daily Sun Protection Guide
Skin Cancer Prevention PDF – free download